After Donald Trump’s surprising 2016 victory over Hillary Clinton, commentators and journalists turned their attention to rural America—where Trump won three times as many votes as his opponent—in order to understand what had just happened. They wrote about forgotten places: small towns populated by opioid addicts, dying Rust Belt cities with abandoned factories at their centers, and mountain hamlets populated by xenophobes and racists. These writers described a conservatism so total and inexplicable that it seemed part of the landscape.
Over the decades, some of these people chose to leave rural America, but more of them were driven out due to policy—agricultural policy, in particular. Republicans and Democrats alike have supported laws that favor corporate agriculture, which continues to drive small farmers out of business and depopulate the countryside. While specialists know this history well, the public tends to know a folk history, written by figures associated with contemporary food movements.
Historians and economists have reached an overwhelming consensus that the New Deal farm bills were designed to aid large farmers, and succeeded in doing so
This folk history rests on several key myths, which cover different periods of modern history from the New Deal to the present. We challenge these myths, not to attack particular authors or engage in pedantry, but to elucidate the causes and extent of the suffering endured by rural families in the 20th century, which, in turn, decimated the populist Left. A reconsideration of the history of agricultural policy will help food-system reformers develop a more radical—and ultimately, more effective—vision for rural America.
Myth: The New Deal was for small farmers
While crop subsidies were an important part of the New Deal, these writers misrepresent the class politics that decided FDR’s agricultural agenda. Over the last 60 years, historians and economists have reached an overwhelming consensus that the New Deal farm bills were designed to aid large farmers and succeeded in doing so: The Agricultural Adjustment Administration (AAA) “accelerated the increasing concentration of land,” writes Pete Daniel, a leading agricultural historian. “Obviously, large landowners reaped most of the federal money.” An aide to Henry Wallace, secretary of agriculture from 1933 to 1940, later said the AAA was “militantly for the larger farmers.” And those farmers benefitted tremendously: government payments increased from 3 percent of net farm income in 1929 to 31 percent by 1940, and farmers’ incomes doubled in the 1930s. These funds went mostly to large-scale operations.
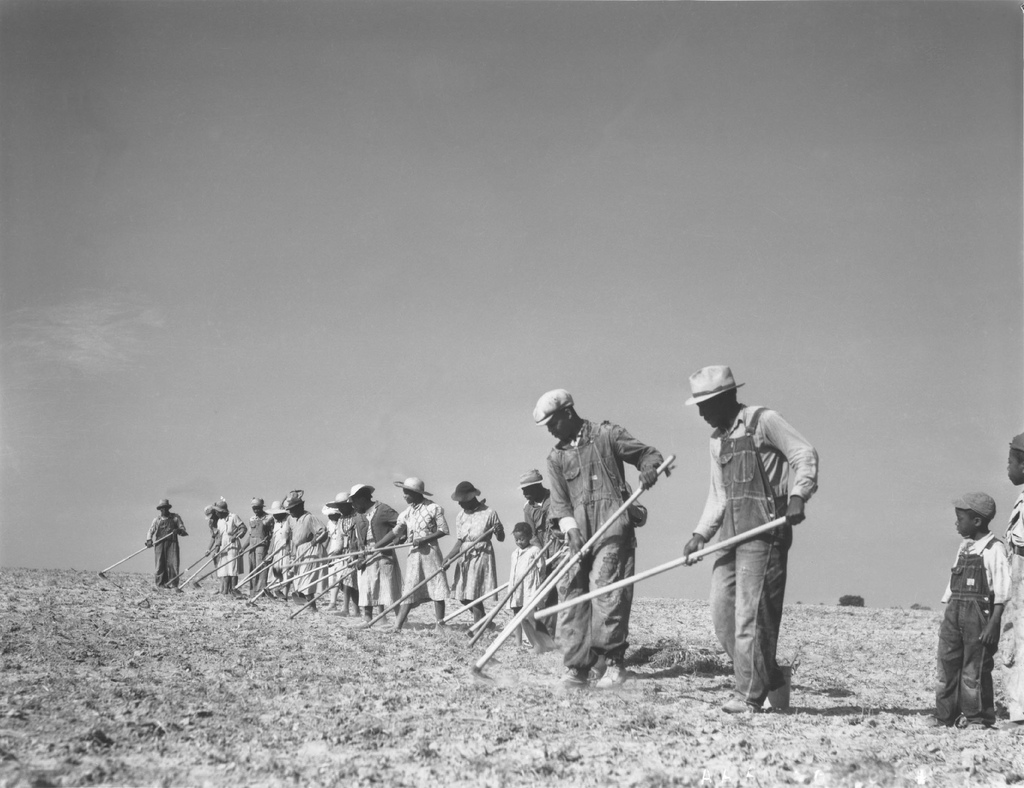
Between 1930 and 1945, the number of white tenants and croppers declined by 37 percent and black tenants and croppers by 32 percent
Meanwhile, farmers, tenants, and sharecroppers were “shoved aside in the rush toward bigger units, more tractors, and less men per acre,” as an official from the Farm Security Administration put it in 1938. As owners of large farms took in more federal money, they were able to acquire more land, mechanize, expel tenants and sharecroppers, and run smaller producers out of business. From 1930 to 1950, the number of farmers declined by 14 percent, with a 37 percent decline for black farmers. Between 1930 and 1945, white tenants and croppers declined by 37 percent and black tenants and croppers by 32 percent. More catastrophic losses were to follow, as the government remained “militantly for the larger farmers” on through the present.
Myth: Black farmers left the South to find better jobs
In reality, historians have established that white Southern leaders encouraged mechanization and co-opted policy in order to pressure blacks to leave. With the backing of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), large farmers cut costs and drove small farmers out of business, while local USDA agents discriminated against black farmers on a systematic basis: by 1920, there were 925,000 black farmers, and by 1970, 90 percent of them were gone. Some of these farmers left for better opportunities, but more were forced out in what the historian Donald Grubbs calls one of the “largest government-impelled population movements in all our history.” When they reached the cities, they entered a white-dominated society where they were treated as inferiors, and “an economy that had relatively little use for them,” as Gavin Wright, an economic historian, puts it, with black unemployment rates between 10 and 15 percent “as early as 1950” and “up to 30 percent” in several major cities, a decade later, writes Michael Munk, a historian.
From 1959 to 1969, the number of black farmers declined by over two-thirds, almost triple the rate of white farmers
As the civil rights movement gathered steam, assaults on black farmers intensified. By the 1950s, writes Gilbert Fite, an agricultural historian, “any program for small, poverty-ridden farmers in the South became entangled with the civil rights movement.” The founder of the Citizens’ Council, reported Bayard Rustin, the civil rights leader, drew up a plan to remove 200,000 African-Americans from Mississippi by 1966 through “the tractor, the mechanical cotton picker … and the decline of the small independent farmers.” As government-funded mechanization continued apace, “tens of thousands” of poor farmers were forced out of agriculture: they eked out an existence in the hinterlands, in shacks, without “food or adequate medical care.”
As Pete Daniel documents in Dispossession, USDA agents withheld loans black farmers needed to operate, denied crop allotments, withheld research and expertise, and overlooked fraud and abuse in elections for powerful local committees that distributed resources to local farmers. From 1959 to 1969, black farmers declined by over two thirds, almost triple the rate of white farmers. The story of black farmers is so thoroughly omitted from the folk history that, in 2014, a writer for Modern Farmer claimed “there are more minority farmers than ever before,” when in reality, there were over nine times as many black farmers in 1920 as there were minority farmers, total, in the 2012 census.
Myth: Earl Butz was a pivotal figure
Butz inaugurated almost none of the programs his critics say he did: they began under earlier USDA chiefs, who had sided with big farmers since the New Deal. Ezra Taft Benson, secretary under President Eisenhower, not Butz, ended production controls for corn in 1959, and was the first to urge farmers to “get big or get out.” Kennedy severely weakened supply management with a farm bill that made programs voluntary for every commodity except wheat. Johnson bragged that his bill would drop prices “to the lowest possible cost” and that he would deal with “farm surplus and supply management” through increased exports, which he expected to grow by “50 percent” in a decade. Johnson’s law also introduced direct payments to farmers, which lasted through the 1980s.
Fencerow-to-fencerow agriculture had been dominant in the Midwest long before Nixon’s Secretary of Agriculture, Earl Butz (center), entered office
Butz’s farm bill was “the logical extension of the acts of 1965 and 1970,” according to former USDA chief economist and Kennedy adviser Willard Cochrane. When that bill passed, monoculture had already taken hold. A series of contemporaneous studies, on the presence of wildlife habitats on farm properties, found that fencerow-to-fencerow agriculture had been dominant in the Midwest long before Butz entered office. “The big fallout of the ‘get big or get out’ mindset,” writes the environmental and agricultural historian James Sherow, “occurred during the Eisenhower, Kennedy and Johnson Administrations.” As Wendell Berry, who inspired Pollan’s food journalism, writes, “Butz’s tenure in the Department of Agriculture, and even his influence, are matters far more transient than the power and values of those whose interests he represented.”
Myth: The farm crisis began in the 1980s
What makes this story so strange is that the decline was significantly slower during the farm crisis, which lasted from 1982 to 1987, than in previous periods. There was a difference, however: a wealthier class of farmers was affected. A group of sociologists who interviewed a representative sample of Iowa farm operators during the crisis found that “persons most at risk of forced displacement from farming are found to be younger, better educated, and large-scale operators.” Wealthier farmers had been much more likely to take out large loans to expand their operations in the 1970s. As a result, when the Federal Reserve suddenly began to curtail inflation in 1979, raising the federal funds rate to a high of 21.5 percent in 1982, these farmers were hit hard by astronomical interest rates.

Source: Census of Agriculture, in Black Farmers in America, 1865-2000
The farm crisis itself was real: families were forcibly and tragically displaced from their farms during the 1980s; the mythmaking begins when writers portray it as a starting point. Numerous families lost their farms prior to the 1980s, often at higher rates, yet their displacement was not perceived as a catastrophe, since they came from marginalized populations, such as rural blacks, Native Americans, and poor whites. By treating the farm crisis as an aberration, these writers conceal this larger tragedy and the decades of policy-making that caused it.
Myth: Land consolidation was inevitable
Between 1930 and 1992, the number of white farmers fell by 65 percent and black farmers by 98 percent, as farms became larger, almost all of them owned by white men. Willard Cochrane ascribed these changes to a “technological revolution.” Jim Chen writes that “technology inexorably increases farm size.” Laurie Ristino and Gabriela Steier, both legal scholars, attribute consolidation to “efficiencies of economies of scale,” the “adoption of tractors . . . and combines,” and “the Green Revolution.” These writers share a sometimes unstated belief in autonomous technological “forces,” part of a discourse of technological determinism rooted in conservative ideology.
“Science does not apply itself, and technology does not introduce itself.”
Since before the New Deal, agricultural planners had advocated for consolidating farmland and mechanizing agriculture. An advisor under Eisenhower, John Davis, coined the term “agribusiness” to describe the vertically integrated, corporate structures that policymakers hoped would come to dominate the production, distribution, and marketing of farm products. While agribusiness proponents believed technology would force small farmers out of business on its own, they advanced policies that favored large-scale producers anyway. As the Monthly Review observed in 1956 when it wrote about concentration in agriculture, “Science does not apply itself, and technology does not introduce itself.” Then, as now, government policy that favored large-scale farmers forced modest growers out of business.
Policy makes politics
While conservatives have consistently pushed more aggressive, pro-agribusiness policies, liberals have often responded with pro-agribusiness policies of their own, even when that meant undermining their own natural allies: small and mid-sized farmers, farm workers, rural minority populations, and the small, independent businesses they support. The Democrats’ approach to agricultural policy has been so perplexing that academics have developed a rich literature, in the field of policy feedback, to understand it. Policy feedback is the study of the ways, as Theda Skocpol recently described it, “in which policy fights and outcomes at one point in time set up, or closeoff, future possibilities.”
As New Deal negotiations began, the Farm Bureau pursued the interests of white, Southern planters, and liberals made significant concessions to them, out of expediency. One of the most significant was “predominant influence” over the administration of the AAA, which the Farm Bureau used to favor large producers and consolidate its power. The group’s membership increased six-fold between 1933 and 1945, as it lobbied for large growers at the expense of smaller farmers. As Mancur Olson concluded in his widely cited study of interest groups, “the Farm Bureau was created by the government.”
From that point on, the Farm Bureau played an expanding role in farm policy, using its increasing power to not only push out small farmers but to oppose progressive legislation at every opportunity. The Farm Bureau, among other things, helped pass the anti-union Taft-Hartley Act in 1947, sought to repeal the federal income tax in the 1950s, bitterly fought Medicare in the 1960s, opposed the Equal Rights Amendment in the 1980s, lobbied against health care reform in the 1990s, and boasted of killing the Waxman-Markey climate bill during President Obama’s first term.
Tom Vilsack, secretary of agriculture under President Obama, is a member of the Farm Bureau and repeatedly spoke at its annual conference during his term
Today, the Farm Bureau and its state branches continue to oppose a wide swathe of progressive legislation. The Farm Bureau’s 2016 list of policy resolutions ran longer than 200 pages and expressed, among other conservative positions, the organization’s opposition to Medicare expansion, universal health care, government-funded high-speed rail, “efforts to remove references to Christmas,” gay marriage, and “special privileges to those that participate in alternative lifestyles.” The Missouri Farm Bureau declared, in 2017, its opposition to the use of “religious legal code,” a euphemistic phrase for Sharia law, in American courts; more stringent gun controls; and a federal minimum wage, all while supporting “right-to-work” legislation, harsher penalties for drug infractions, and a constitutional amendment requiring a balanced federal budget.
Vilsack is one in a line of Democratic politicians who have supported conservative policies that undermine their own party. If Democrats want to win more rural voters, they must develop and articulate an alternative, and progressive, rural policy. There are signs that this may be starting to happen. Family Farm Action, an advocacy group of progressive family-farmers, is attempting to rally small farmers and rural communities against the behemoth firms that dominate the American countryside. But since most people in rural areas are not farmers or farm workers, Democrats will need to expand their reach. Rather than funneling cash to large-scale farmers and corporations, Democrats should support workers and small-scale businesses. Rather than displacing poor and marginalized rural people, the party must empower them. As history has shown, to do otherwise would be not only disastrous for the party, but for the nation as a whole.